AI Threat Detection: Revolutionizing Cybersecurity
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the battle between cybersecurity professionals and malicious actors has reached unprecedented levels of sophistication. AI threat detection is emerging as a game-changing technology in this ongoing struggle, providing organizations with powerful new capabilities to identify and neutralize cyber threats before they can cause damage. As cyber attacks grow more complex and frequent, traditional security approaches are struggling to keep pace, making artificial intelligence a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies.
Estimated Reading Time
7 minutes
Key Takeaways
- AI threat detection is pivotal in modern cybersecurity due to its adaptive capabilities.
- Machine learning provides the underpinning for detecting complex threats with high accuracy.
- Real-time monitoring and automated anomaly detection enhance security posture.
Table of Contents
- Understanding AI Threat Detection
- The Role of Machine Learning in Threat Detection
- Real-Time Threat Monitoring through AI
- Automated Anomaly Detection
- AI-Powered Intrusion Detection Systems
- AI for Predictive Threat Intelligence
- Enhancing Security Operations with AI
- Challenges in AI Threat Detection
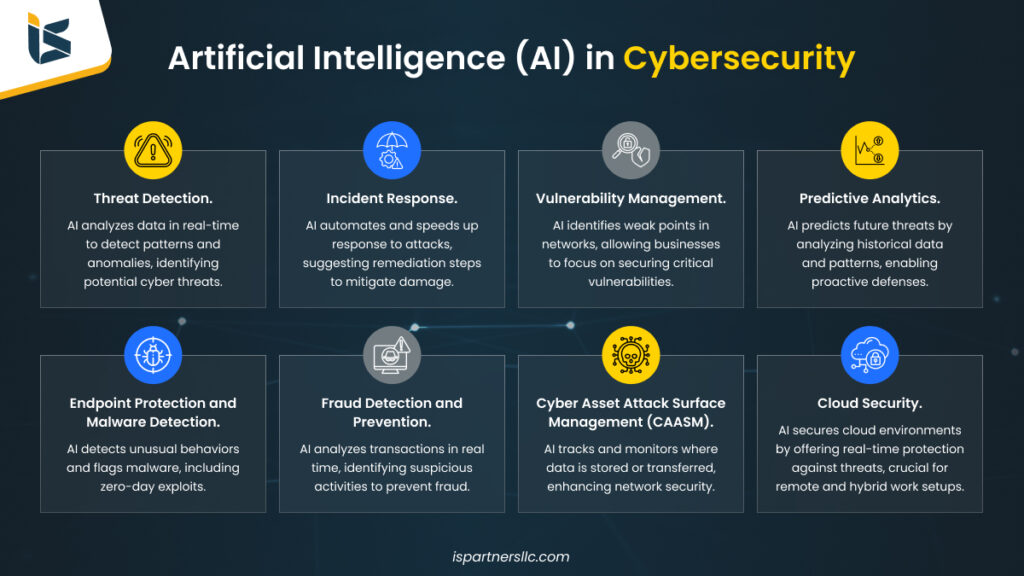
Understanding AI Threat Detection
AI threat detection leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to identify, analyze, and respond to potential security threats in real-time. Unlike conventional rule-based security measures that rely on known signatures and patterns, AI-powered systems can adapt to new and evolving threats, making them far more effective at identifying previously unknown attack vectors.
- Process massive volumes of data quickly
- Detect subtle patterns and anomalies
- Learn and improve continuously
- Adapt to evolving threat landscapes
These intelligent systems work by constantly analyzing data from diverse sources, including network traffic, user behavior, application logs, and system activities. Using advanced pattern recognition and anomaly detection techniques, AI can swiftly identify suspicious activities that might indicate a security breach, often before traditional systems would even notice.
The Role of Machine Learning in Threat Detection
Machine learning, as a subset of artificial intelligence, serves as the backbone of modern threat detection systems. ML algorithms excel at processing and analyzing enormous datasets at high speeds, enabling quick identification of potential security issues. These advanced algorithms learn from historical data and continuously refine their accuracy, allowing them to detect increasingly subtle and complex attack patterns.
- Malware Detection and Classification: ML algorithms can identify previously unknown malware by recognizing subtle code patterns and behaviors similar to known threats.
- Phishing Attack Identification: AI systems can analyze email content, sender information, and embedded links to detect sophisticated phishing attempts that might bypass traditional filters.
- Network Intrusion Detection: Machine learning models monitor network traffic to spot unusual patterns that may indicate unauthorized access attempts.
- User Behavior Analysis: AI can establish baselines of normal user behavior and flag deviations that might represent account compromise or insider threats.
Machine learning’s iterative improvement makes it particularly valuable in cybersecurity, where threat actors constantly develop new tactics and techniques. As these systems encounter more data and security incidents, they become increasingly adept at distinguishing genuine threats from benign activities.
For more details, visit here and here.
Real-Time Threat Monitoring through AI
In today’s fast-paced threat environment, real-time monitoring capabilities are essential for effective cybersecurity. AI-powered systems excel at continuous surveillance by analyzing data streams as they flow, detecting potential threats the moment they emerge. This rapid identification allows organizations to respond to security incidents promptly, minimizing potential damage and substantially reducing the risk of successful attacks.
- Speed: AI can analyze millions of events per second, identifying threats in milliseconds rather than hours or days.
- Accuracy: Advanced algorithms can distinguish between normal fluctuations and genuine security concerns, reducing false positives.
- Scalability: AI systems can effortlessly handle expanding data volumes as organizations grow.
- Continuous Learning: These systems constantly improve their threat detection capabilities based on new data and outcomes.
With cyber attacks becoming increasingly time-sensitive, the ability to detect and respond to threats immediately rather than during a subsequent security review can make the difference between a minor security incident and a major data breach.
Learn more from this resource.
Automated Anomaly Detection
One of the most powerful capabilities of AI threat detection systems is automated anomaly detection. By establishing baseline patterns of normal behavior across networks, systems, and users, AI can quickly flag deviations that may signal a security threat. This approach is particularly effective because it can identify novel threats that signature-based systems would miss entirely.
- Unusual Network Traffic Patterns: Sudden spikes in data transfer, unexpected connection attempts, or communication with suspicious domains.
- Suspicious User Activities: Logins at unusual times, access to resources not typically used, or abnormal patterns of file access.
- Unexpected System Behavior: Unusual resource utilization, unexpected configuration changes, or anomalous process activities.
- Potential Data Exfiltration: Patterns of data movement that might indicate someone is attempting to extract sensitive information.
This capability is essential for detecting advanced persistent threats (APTs) and sophisticated attacks that deliberately avoid triggering traditional security alarms. By focusing on behavioral anomalies rather than known signatures, AI can spot the subtle indicators of complex, multi-stage attacks.
More information is available here.
AI-Powered Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems have been transformed by artificial intelligence integration. While traditional IDS rely on predefined rules and signatures to identify known threats, AI-powered systems can detect novel attack patterns and adapt to evolving threat landscapes. This capability is crucial in an environment where new vulnerabilities and exploit techniques emerge constantly.
- Zero-Day Exploit Detection: AI can identify previously unknown exploits by recognizing suspicious patterns of behavior, even without specific signatures.
- Reduced False Alarms: Machine learning algorithms can better distinguish between legitimate activities and actual threats, decreasing alert fatigue among security teams.
- Advanced Threat Recognition: AI-powered IDS can detect sophisticated, multi-stage attacks by correlating seemingly unrelated events across different systems.
- Continuous Improvement: These systems become more effective over time as they encounter and learn from new attack vectors.
The combination of traditional rule-based detection with AI-driven behavioral analysis creates a more comprehensive security posture, allowing organizations to detect and respond to both known threats and novel attack methods.
Read more here.
AI for Predictive Threat Intelligence
Beyond detecting active threats, AI is revolutionizing predictive threat intelligence by analyzing trends, vulnerabilities, and attacker behaviors to anticipate future security risks. This forward-looking approach enables organizations to strengthen defenses before attacks occur, shifting from reactive to proactive cybersecurity.
- Threat Actor Behavior Analysis: Identifying patterns in how specific threat groups operate to predict their likely future targets and methods.
- Vulnerability Prioritization: Using historical data to determine which security weaknesses are most likely to be exploited, allowing better allocation of remediation resources.
- Attack Surface Monitoring: Continuously evaluating an organization’s external footprint to identify new potential entry points before attackers do.
- Emerging Threat Recognition: Analyzing global threat data to spot new attack techniques as they first appear in the wild.
By leveraging these predictive capabilities, security teams can make more informed decisions about where to invest their limited resources, focusing on the vulnerabilities and threats that present the most significant risks to their specific environments.
Enhancing Security Operations with AI
AI is transforming security operations centers (SOCs) by augmenting human analysts’ capabilities and automating routine tasks. This enhancement allows security teams to focus on complex issues that require human judgment while AI handles the high-volume, repetitive aspects of security monitoring.
- Alert Triage and Prioritization: AI can categorize and prioritize security alerts based on severity, reducing the overwhelming volume of notifications analysts must process.
- Automated Investigation: AI systems can gather relevant context around security events, correlating information from multiple sources to create comprehensive incident timelines.
- Response Automation: For common threat scenarios, AI can initiate predetermined response actions, containing threats faster than human-only teams.
- Knowledge Management: AI can capture and organize institutional knowledge, making it easier for security teams to access relevant information during incidents.
These capabilities help address the chronic shortage of cybersecurity professionals by multiplying the effectiveness of existing teams and reducing burnout from repetitive tasks and constant alert fatigue.
Challenges in AI Threat Detection
Despite its transformative potential, AI threat detection faces several significant challenges that organizations must address to maximize its effectiveness:
- Adversarial Attacks: Sophisticated attackers can deliberately manipulate AI systems by introducing specially crafted inputs designed to cause misclassification or other unintended behaviors.
- Data Quality Requirements: AI systems need large volumes of high-quality training data to perform effectively, which can be difficult to obtain, especially for rare attack types.
- False Positive Management:
Explore more on this platform.
